Explore insights and innovations in
healthcare through our blog, where
experts share their knowledge and
experiences, aiming to inspire and inform
our readers.
Explore Products
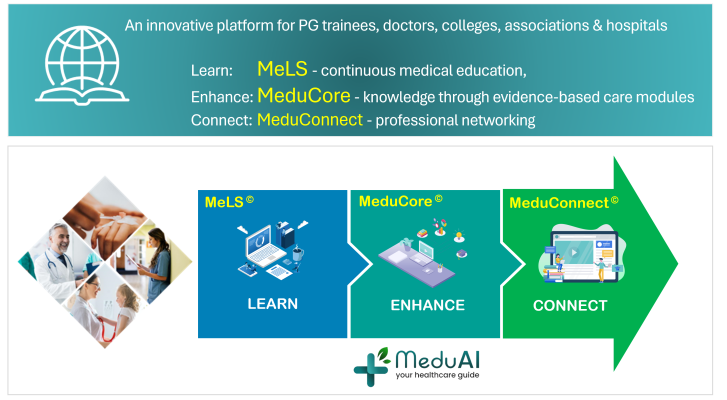
Medusys empowers the healthcare community to learn, enhance and connect

.png)